VitalSource and Hypothesis Partner to Expand Social Learning

Hypothesis and VitalSource have collaborated to bring the first-ever integration of a third-party social learning tool directly into a leading digital reading platform.
Through our partnership, schools and educators using any e-reader powered by VitalSource Bookshelf will be able to add Hypothesis social annotation to any reading, enabling students and teachers to hold threaded conversations in the margins, anchored directly in specific passages of texts. Turning on Hypothesis annotation makes reading more active, more visible, and more social, generating new pathways for teachers and students to amplify and enrich their engagement with content and with each other in both on-campus and online classrooms.
This new integration is the first collaboration growing out of Social Learning Across Content (SLAC), a coalition of content platforms, publishers, tool providers, schools and other stakeholders working toward a vision where social learning can take place anywhere; across any platform or vendor.
Making Hypothesis available within VitalSource’s Bookshelf reading environment exemplifies SLAC’s goal of supporting interoperability for social learning across all content.
“Students and teachers want powerful, universal capabilities for social learning across all their digital texts, from textbooks to other course materials, video and the web itself. Our work together shows that social learning properly implemented improves engagement dramatically,” says Dan Whaley, Hypothesis CEO.
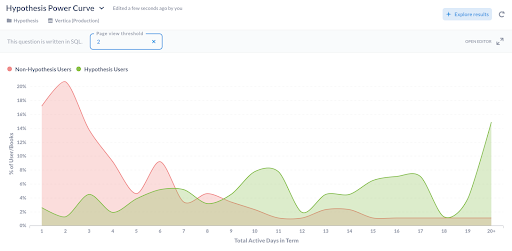
With Hypothesis, students were active in the text on substantially more days than without it.
Initial results from a spring 2022 trial show that by bringing Hypothesis and VitalSource together, more students read assigned texts, and engage with their reading more often and longer than students assigned the same texts without social annotation. This data supports what educators are already saying about reading socially: Embedding conversations directly in texts leads students to read more, to increase the depth of their reading, to build community with their classmates and teachers, and to make more connections across readings and classes, ultimately supporting their academic progress and success.
“[My students] had annotation assignments they had to do to get points,” says Allison Brenneise, Lecturer at University of Minnesota-Twin Cities. “But what surprised me was that they were pulling examples and quoting content from the book in other assignments as well and that really says that they were reading the book more than before.”
By partnering with VitalSource, Hypothesis can now offer social annotation in more places for more students — adding over 16 million VitalSource users in more than 240 countries — across a vast new quantity of content: over a million texts from over a thousand publishers available in the Bookshelf platform.
“It’s no secret that getting students to complete their assigned readings is a challenge. We’ve invested heavily in making Bookshelf the best way for students to get the most out of their textbook to try to solve that problem. But to date, Bookshelf has largely been used for studying alone,” says Nick Brown, VP, Product at VitalSource. “Partnering with Hypothesis gives us a great opportunity to explore what student engagement with the textbook looks like when we add social learning to the mix, and the early signs are very promising. I’m excited to see student engagement continue to thrive as we power more courses together.”
Leading the way for a new era of social learning, VitalSource was able to add the most widely used social annotation tool to their entire content catalog quickly and easily by integrating Hypothesis’ interoperability and standards-compliant open-source toolset.
Start using Hypothesis in your LMS and learn more about pricing for your school.